Find the right way to turn up the heat with our guide on the best types of central heating systems for homes.
Navigating the landscape of central heating systems in the UK can be a complex task, given the numerous options available. In this article, we will explore the various types of heating systems, from traditional boilers to underfloor heating solutions. We will explore the different types of heating systems for UK homes, focusing on their functionality, efficiency, and suitability for UK climates.
Before we continue, be sure to learn how central heating has changed everything about our homes.
Selecting The Right Heating System
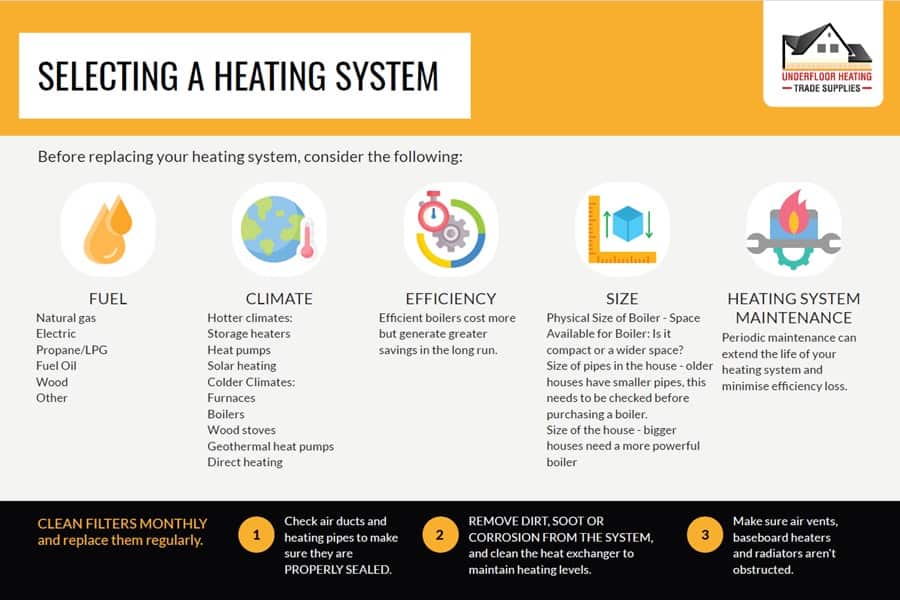
With so many heating systems to choose from, it can be hard to figure which one is best for your home. Ensure to consider these factors when choosing the right type of heating system for your home.
Fuel Choices
The type of fuel accessible for heating systems varies across the UK. In areas like the Northeast, heating oil prevails due to the scarcity of natural gas. Understanding local fuel availability is crucial in selecting an appropriate heating system.
Climate Considerations
Your local climate significantly influences the choice of heating system. Milder regions may only require space heaters, whereas colder areas need robust central heating systems to ensure consistent warmth throughout the home.
Efficiency and Cost
Efficiency is a key factor in selecting a heating system, as more efficient units typically entail lower running costs despite higher initial expenses. Opting for ENERGY STAR-certified systems can guarantee efficiency and quality, providing long-term savings.
Sizing the System
Appropriate sizing of the heating system is essential. An oversized system can lead to increased operational costs. Consulting with a heating expert can help determine the ideal size for your home, ensuring better performance and efficiency. To make the most use of your space, a room planner is a great tool to use.
Maintenance Matters
Regular maintenance is vital to sustain the efficiency and longevity of your heating system. Monthly filter cleaning, checking for sealed air ducts, and ensuring the cleanliness of the heat exchanger are all important practices to maintain heating efficacy.
Heating System Types
Various types of heating systems cater to different needs and preferences in the UK. these are the most popular types of heating systems in the country:
- Traditional boilers
- Combi boilers
- Heat pumps
- Gas-fired space heaters
- Oil central heating
- LPG central heating
- Underfloor heating
Find out about the intricacies of these systems and many more below.
What is HVAC?
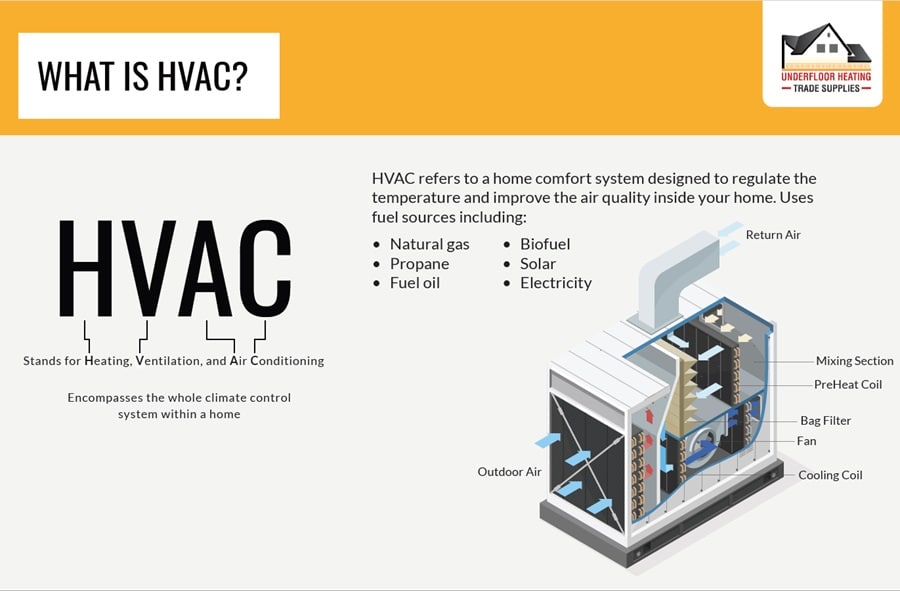
HVAC stands for:
- Heating
- Ventilation
- Air Conditioning
This abbreviation encapsulates the systems that control the climate within a building. These systems provide comfort by regulating indoor temperatures, airflow, and humidity levels. HVAC systems can utilise various fuel sources like natural gas, propane, fuel oil, biofuels, solar energy, and electricity, adapting to different energy needs and preferences.
Central Heating Systems Explained
Central heating systems are pivotal in UK homes, offering warmth and comfort. These systems are diverse, ranging from traditional boilers to modern heat pumps, each with unique benefits and efficiencies.
Conventional Heating Systems
Conventional systems, often found in older homes, use a gravity-fed mechanism where a water tank, typically located in an attic, supplies hot water throughout the house. These systems are straightforward but may face limitations in pressure and energy efficiency.
Pressurised Heating Systems
On the other end, pressurised systems provide hot water at mains pressure from a cylinder placed anywhere in the property, offering a consistent water flow and higher efficiency. These systems are ideal for larger homes or businesses needing a reliable hot water supply.
1. Boilers
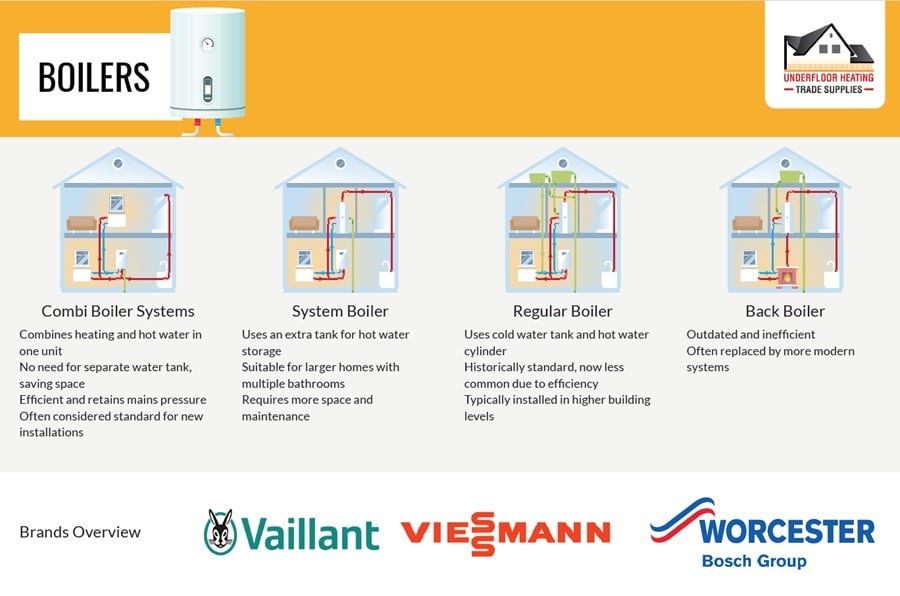
Boilers are the most economic form of central heating – every home, either period, renovated, new, or contemporary, will undoubtedly have one, but the complexities of a boiler stretches beyond common knowledge. Here is important information to consider about each type of boiler.
Combi Boiler Systems
Combi boilers represent a significant advancement in central heating systems, offering efficient and space-saving solutions. These systems heat water directly from the mains, eliminating the need for a storage tank and ensuring hot water on demand. Their compact size and efficiency make them a popular choice in UK homes, aligning well with the varying types of heating systems for homes. Combi boilers are versatile, available in gas, electric, or oil variants, catering to different home setups and energy preferences.
Regular Boilers
Regular, or heat-only boilers, are traditional systems that work with a cold water tank and hot water cylinder. Though less common in new installations, they remain a reliable option for homes with existing suitable infrastructure, offering steady hot water supply but at the cost of higher space and energy requirements.
System Boilers
System boilers, akin to combi boilers but with an additional hot water tank, provide a continuous hot water supply, making them ideal for larger homes or multiple bathroom properties. While they occupy more space than combi boilers, their ability to meet higher hot water demands efficiently makes them a favourable choice for bigger households.
Outdated Back Boiler
Back boilers, once common, are now largely obsolete due to their inefficiency and bulky design. Typically hidden behind a fireplace, these units are now replaced by more modern and efficient systems, with combi and system boilers offering superior heating control and space efficiency.
Gas vs Electric
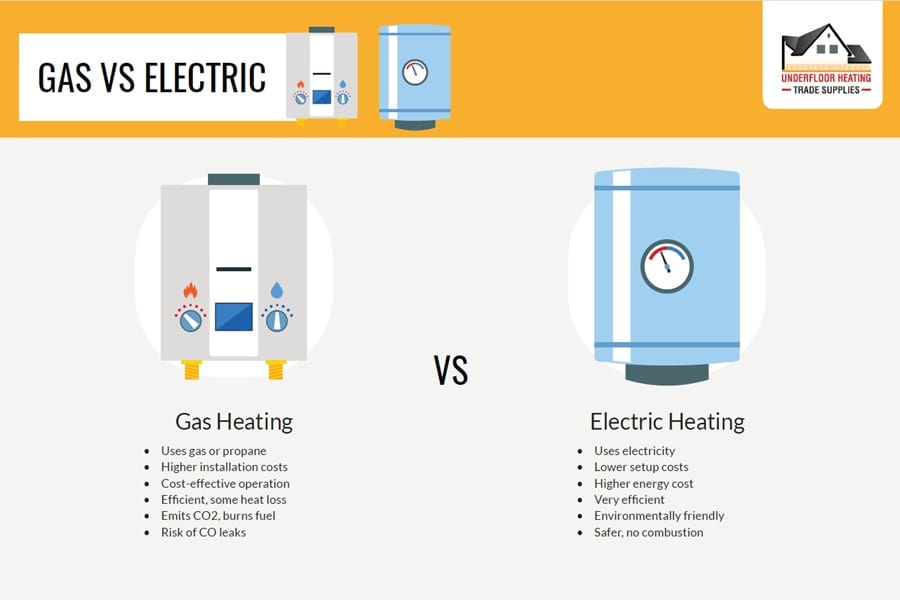
In the UK, the battle between gas and electric central heating systems continues, with each offering distinct advantages and challenges. Gas has traditionally dominated the market, known for its reliability and cost-effectiveness. However, electric heating is gaining traction, lauded for its efficiency and environmental benefits.
Gas Boilers
As shown above, gas boilers are a staple in UK homes, using a network of pipes to distribute hot water to radiators. They are valued for their ability to provide consistent heat and are typically cheaper to run than electric boilers, especially in areas with access to mains gas. Gas systems require a boiler that operates continuously, ensuring a steady flow of heated water throughout the home. While they are cost-effective and efficient, gas boilers depend on fluctuating gas prices and require regular maintenance.
Advantages of Gas Heating
- Cost-effective in the long run
- Consistent and reliable heating
- High efficiency, especially with condensing models
Electric Boilers
Electric boilers are becoming more popular, thanks to their near 100% efficiency rate and minimal space requirements. They are particularly suitable for smaller homes or areas where gas is not readily available. Electric boilers heat water on demand, reducing energy wastage and offering a more environmentally friendly option.
Advantages of Electric Heating
- Higher efficiency with less energy wastage
- Environmentally friendly, with no emissions
- Less maintenance and no need for a flue or gas supply
Leading Boiler Brands in the UK
Vaillant:
Vaillant stands out with its ecoTEC range, particularly the ecoTEC Plus and Exclusive models, celebrated for their energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact. These units are renowned for their silent operation and user-friendly controls.
Viessmann:
Viessmann’s Vitodens series, like the 100-W and 200-W, offer compact, high-efficiency heating solutions with durable Inox-Radial heat exchangers and smart thermostat compatibility, providing both control and convenience.
Alpha:
Alpha’s E-Tec range, especially the E-Tec Plus, strikes a balance between cost and performance, offering energy-efficient and compact boilers suitable for a range of home sizes.
Ideal:
Ideal Boilers, known for the Logic Plus range, are prized for their efficiency, ease of use, and straightforward maintenance, backed by comprehensive warranties for reliability.
Worcester Bosch:
Worcester Bosch’s Greenstar series exemplifies efficiency and durability, integrating smart controls and robust construction, maintaining their status as a preferred choice in UK homes.
2. Electric Heating
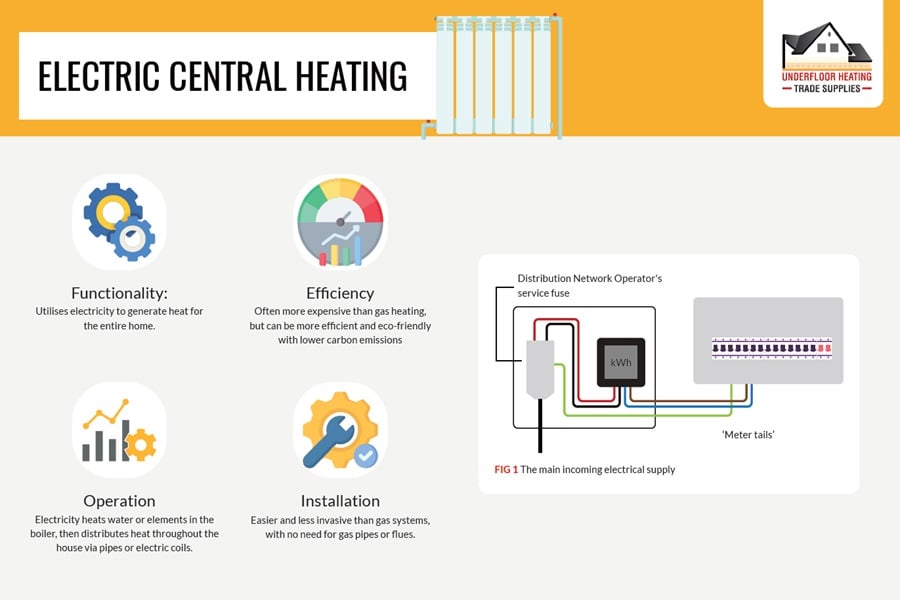
Electric central heating is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of home heating in the UK, especially as the nation moves towards reducing fossil fuel usage. While currently more expensive than gas, electric heating presents a viable option for those producing their own electricity via solar panels. These systems are most popular in new builds and flats, offering a cleaner, albeit costlier, alternative to traditional gas heating.
3. Infrared Heating Systems
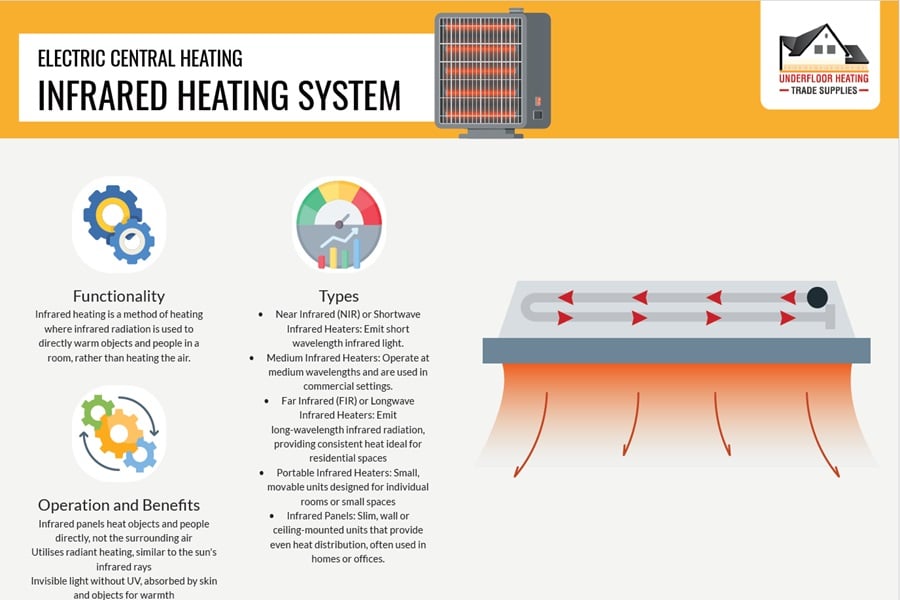
Infrared heating, a newer technology in the UK market, directly warms objects and people, offering an efficient alternative to traditional heating methods. This system boasts health benefits like improved air quality and reduced dampness, avoiding the circulation of dust and allergens. With various stylish designs, infrared panels can enhance home aesthetics while providing cost-effective heating. These systems, possibly powered by renewable sources like solar panels, represent a significant step towards sustainable home heating.
Learn about how heating systems can prevent allergies with our advice on heat and asthma.
4. Renewable Heating
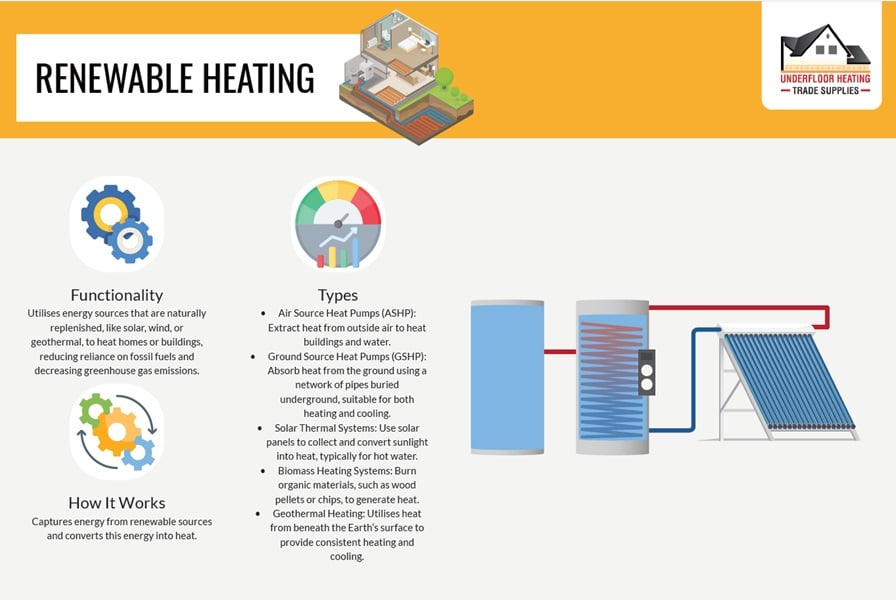
Renewable heating solutions are gaining popularity, with homeowners increasingly adopting systems like heat pumps, solar water heaters, and biomass boilers. These technologies not only diminish the reliance on fossil fuels but also aim to reduce the environmental footprint of residential heating.
5. Solar Panel Water Heating Systems
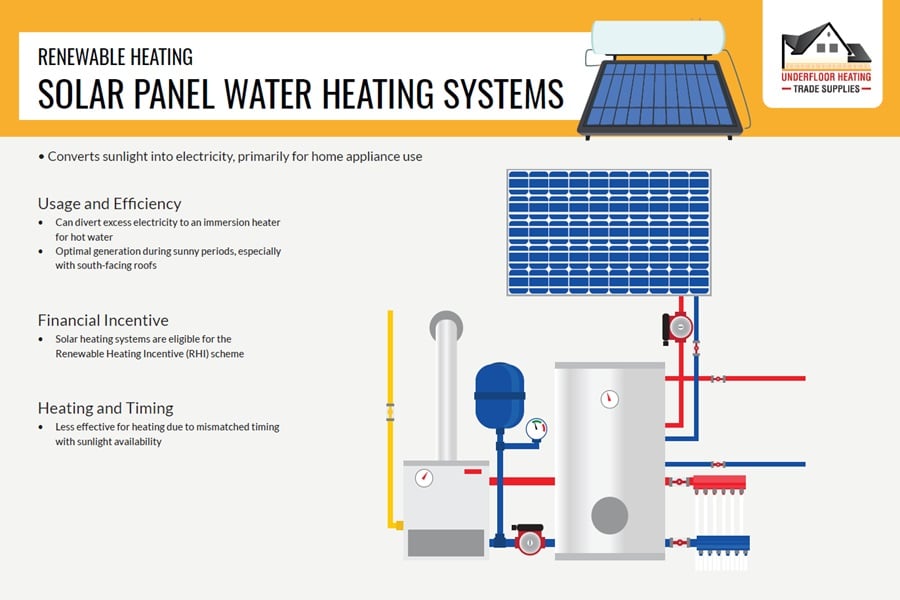
Solar panel systems harness sunlight to generate electricity, offering an eco-friendly solution to home heating. While primarily used for powering appliances, surplus energy can heat water, aligning with the Renewable Heating Incentive scheme. This makes solar heating an attractive option for those with south-facing roofs, blending sustainability with practicality.
6. Heat Pumps
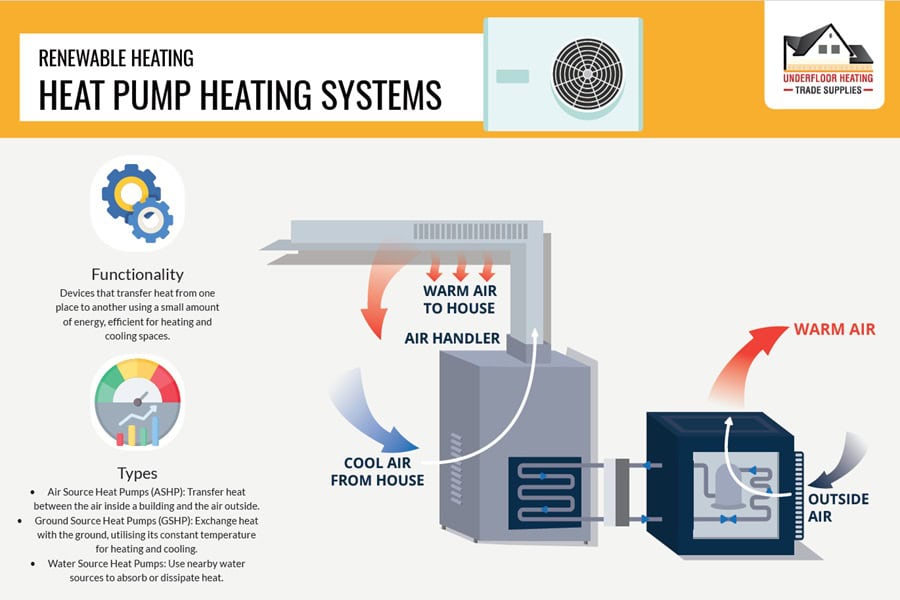
Heat pumps represent the cutting edge in central heating systems, efficiently providing both heating and cooling. These systems work by extracting heat from air, ground, or water sources, making them suitable for various UK climates. Air-source and ground-source heat pumps offer an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for homes, blending seamlessly with the environment and modern energy needs.
| Pros | Cons |
| Easy combination with heating and cooling without duck tape Energy-efficient Specific temperature control throughout each room | Better for mild climates Limited distribution of hold and cold air Separate room units are required |
7. Hybrid Heat Systems
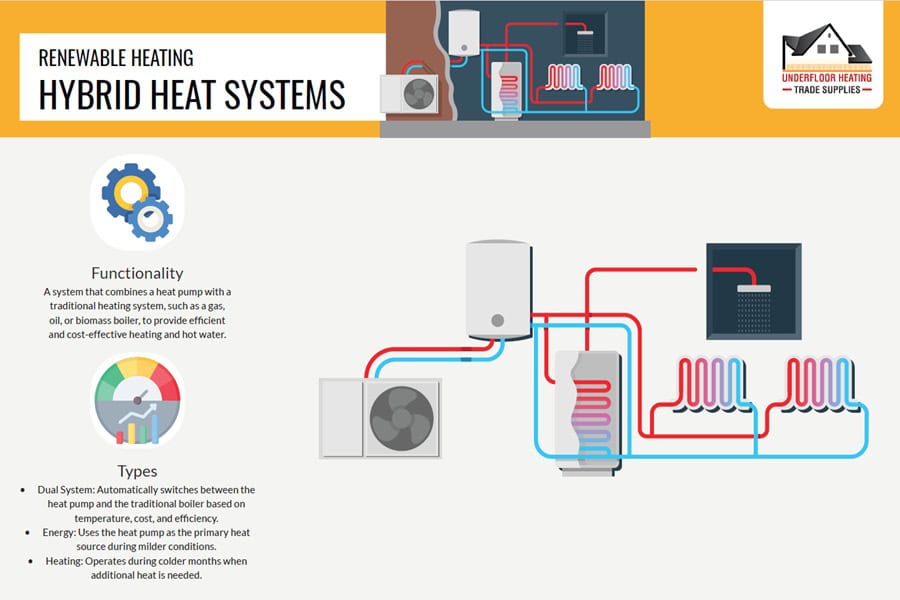
Hybrid heat systems, merging electric heat pumps with gas furnaces, offer a versatile solution for UK homes facing fluctuating temperatures. These systems smartly alternate between heat sources, using the pump for milder conditions and the furnace for colder spells, ensuring efficient and consistent heating tailored to seasonal changes.
| Pros | Cons |
| More efficient Can easily produce heat in the winter Furnace will work automatically in cold weather | Not suitable for warm regions Two systems require maintenance Higher Installation costs |
Mix and Match Heating for Multi Zone Heating
Adopting a mix-and-match approach to heating can offer flexibility and efficiency, allowing homeowners to combine different heating types across various spaces and times. This is otherwise known as multi-zone heating. This strategy enables the gradual incorporation of renewable energy sources, reducing carbon emissions over time. With the ongoing green transformation of the National Grid, even homes connected to mains electricity are set to experience a decrease in their carbon footprint.
8. Underfloor Heating
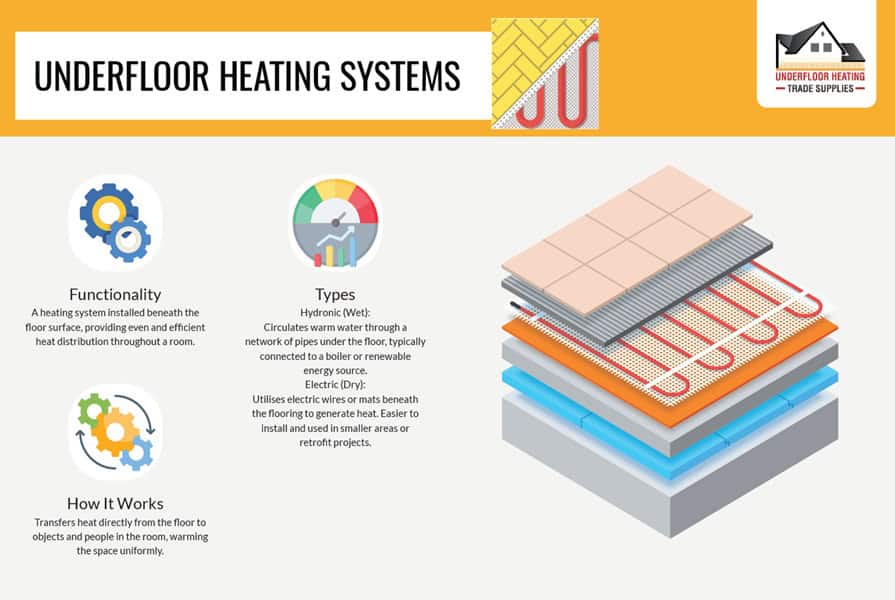
Underfloor heating systems offer a modern approach to heating, ideal for homes in areas with milder winters. This method uses water tubes or electric wires (otherwise known as electric underfloor heating and water underfloor heating) beneath the floor to provide consistent and energy-efficient warmth, directly heating objects and surfaces rather than the air. Much like the other central heating systems on this list, its important to hire a professional when installing underfloor heating.
There are some rumours circulating the dangers of underfloor heating; learn more about them now.
| Pros | Cons |
| Comfortable, evenly distributed heat More energy efficient when combined with boilers Can be solar-powered | Slow heat up time Expensive installation Difficulty in maintaining hidden piping |
9. Air Furnace Systems
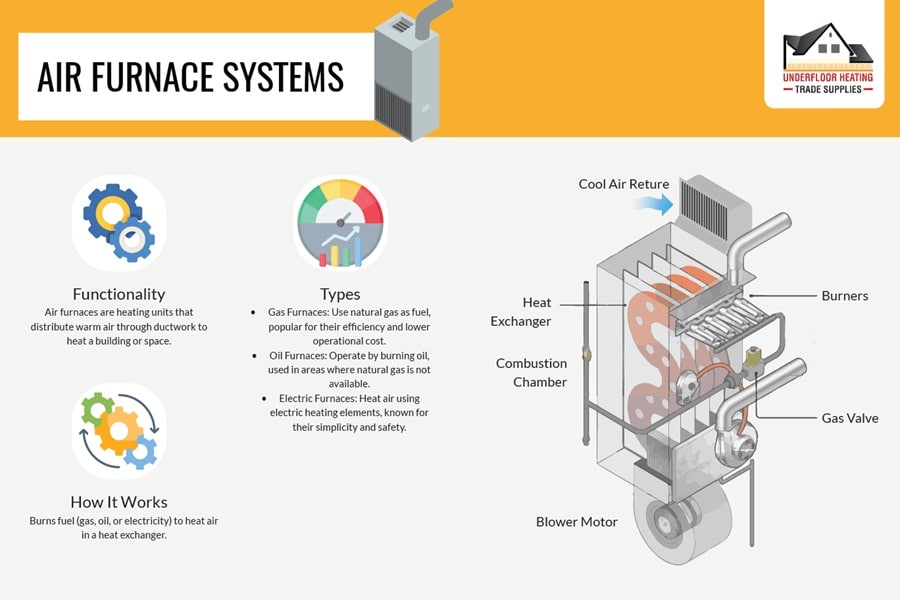
Air furnace systems, especially gravity air furnaces, provide a durable and low-maintenance heating solution. Utilising the natural movement of warm and cool air, these systems deliver heat throughout the home via ductwork, offering a reliable and time-tested method of central heating in many UK homes.
| Pros | Cons |
| No moving parts Can last for decades Requires little maintenance Quiet operation | Weak air filtration Less energy-efficient Slow to adjust temperature |
10. Wood Heating Systems
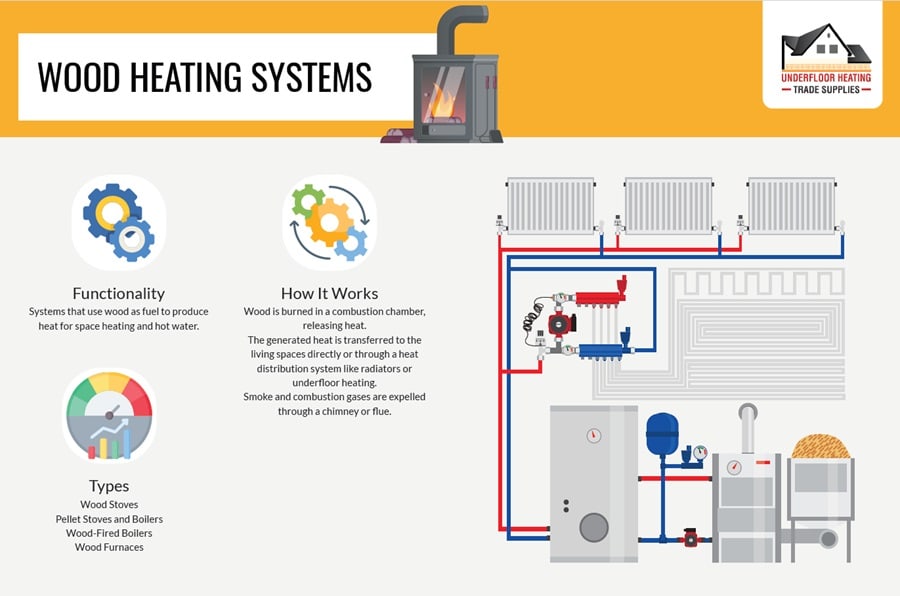
Wood heating systems, such as wood stoves, pellet stoves, and outdoor wood boilers, offer a cost-effective and sustainable option for UK homes. These systems provide a reliable source of heat, using renewable resources like wood logs and pellets. Ideal for those seeking a traditional heating method, they combine the charm of a real fire with the efficiency and control of modern heating technology.
| Pros | Cons |
| Cleaner burning technologies available Wood is a cheaper fuel source Great for emergencies and power outages Long-lasting lifespan (20-50 years) | Fire hazards when not used or installed properly Potential health problems from smoke emissions Poor circulation due to trapped heat Pellet stoves require generators to prevent power outages |
The Best of Central Heating Systems..
By now, you should have a clearer idea and incentive about each type of central heating system available in the UK. With cleaner and more efficient heating system methods suitable for any type of home, you can be rest assured that, amongst all of these heating systems, underfloor heating is by far the most suitable and is more likely to last longer in your home, thereby reducing your carbon footprint too.
FAQs
What are the 4 types of central heating systems?
The four types of central heating systems are gas heating, oil heating, electric heating, and renewable energy systems like solar-powered or geothermal heating.
What is the most efficient heating system for your home?
The most efficient heating system for a home is typically a geothermal heat pump, as it uses the stable temperature of the earth to heat and cool the home, leading to lower operating costs.
What is the most common heating system in the UK?
The most common heating system in the UK is a gas boiler system, which heats water that is circulated through radiators in the rooms.
Sources
Johnson-Schlee, S., (2024). How central heating changed everything about our homes. Financial Times. [online] Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/9632c12c-1153-4f0f-acef-cbfe4b63ec58 [accessed 26/03/24]
Energy Saving Trust. (2023) Renewable Heat Incentive. [online] Available at: https://energysavingtrust.org.uk/grants-and-loans/renewable-heat-incentive/ [accessed 26/03/24]
